
Redegal, Google Partner Premier agency 2025
RDG 6.95 €
A website is a cornerstone of any company’s communication strategy. That’s why we’re sharing the essential elements it should have, the benefits for your business, and how to build one in just five simple steps.

In today’s digital landscape, a website is essential for a company’s success. It provides users with key information about your business and serves as a go-to resource for customer inquiries about your products or services. That’s why it’s crucial to develop a well-structured site, define its key components, and implement a strong digital strategy to maximize visibility in search engines.
A SWEOR report estimates that it takes a person about 0.05 seconds to form an opinion about a website. This is why a website must be attractive, clear, and simple. The more visual and intuitive its navigation and information searches are, the higher the probability that users will stay on it or return more frequently in the future.
While the content on your website is crucial, its design is the key to captivating your audience. Discover how to enhance your site’s design to engage visitors and keep them around longer—read on for expert tips!
The structure of a website will ensure that content is organized and that the audience can quickly and easily find what they are looking for. Within this structure, various elements make up the website. However, some are necessary for proper functionality and are therefore repeated across all websites. These indispensable elements form the backbone of every effective website, and include:
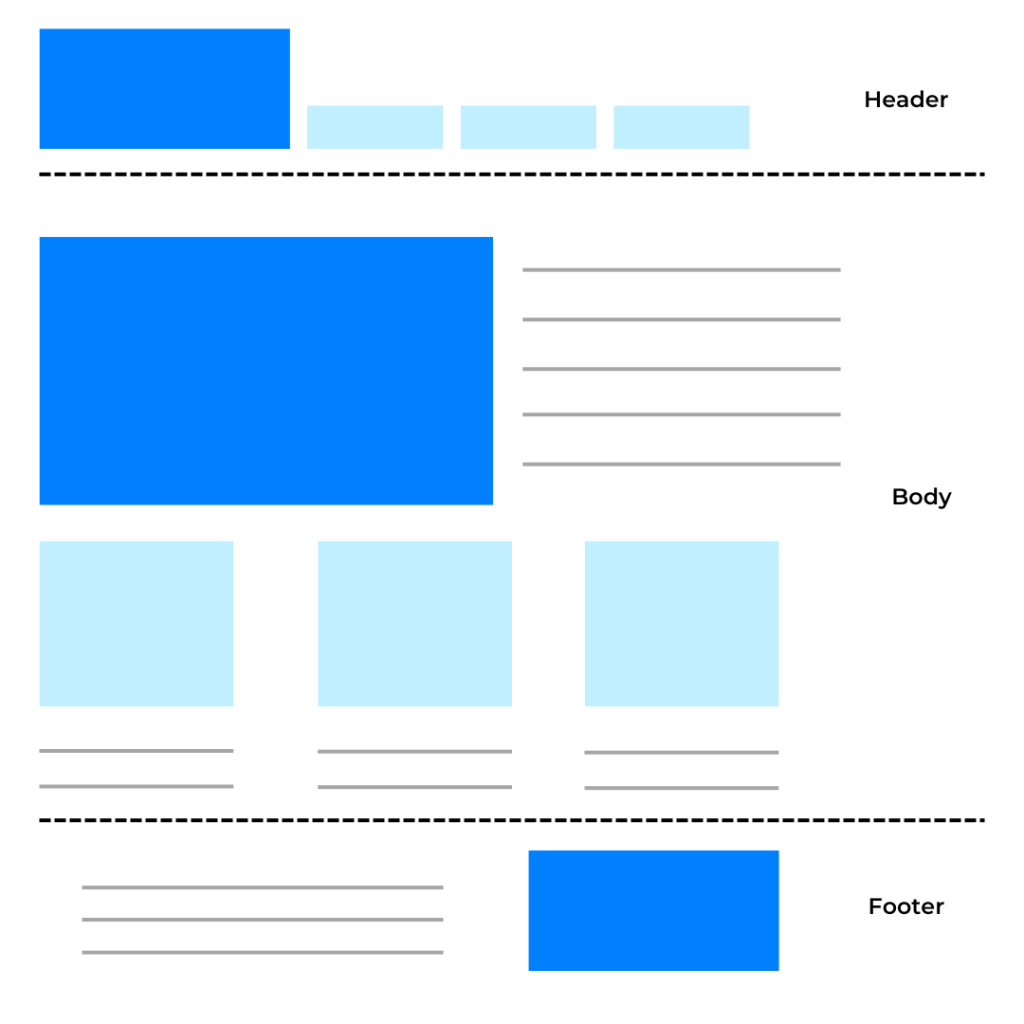
The header refers to the <head></head> section of the code. It contains meta information about the page and the navigation menu. Visually, its content is located at the top of the website. It’s the first thing users see when they arrive at the site. The design should help users stay, so it should be simple and visual, allowing them to easily find what they are looking for. If the design is complex and confusing, making it difficult to filter information, users are likely to get frustrated and leave the site.
The content should be written in a clear and readable font, all subpages should be easily displayed, and the design should be consistent with the rest of the website.
Additionally, you can make this header fixed so that it remains visible as users scroll and navigate through your website. This provides greater convenience, speed, and ease, as users won’t have to scroll back up to find the header.
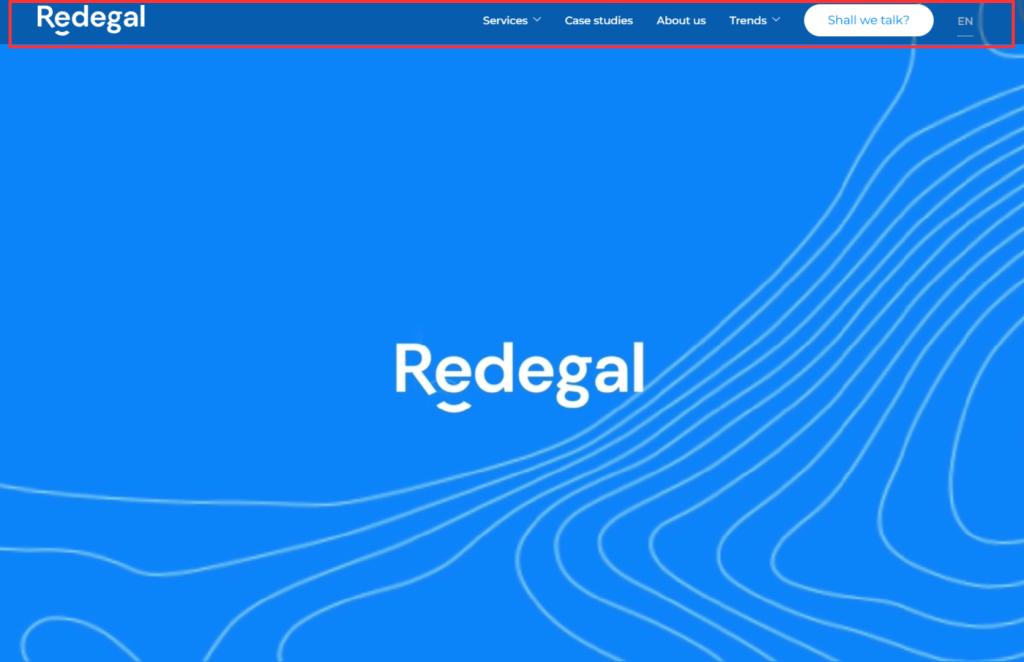
Here we share an example, highlighted in red, of a header using our tool Binnacle Data, which allows you to measure and monitor metrics to improve the performance of your digital business.

For an e-commerce or online store, the header should also include:
The menu can be understood as the “map” that helps users find what they are looking for. It organizes content and directs the user’s flow within the website. Menus can vary in type and location, such as:
To facilitate navigation, the menu should have a logical and intuitive structure. It is also advisable to keep it concise and clear, with 4-7 options, making searches easier for visitors. You can create general categories that contain related subcategories. For example, if you have a sportswear e-commerce site, you can create a “Products” category that expands into different types of clothing.
Some of the information that can be added to the header to facilitate user interaction includes:
In the case of Redegal, the menu (highlighted in red) consists of five categories, which in turn include other subcategories to make it as visual and intuitive as possible for the user.
The website’s body—the central content section—is the heart of your site. It should showcase your brand’s essential information in an engaging way. It’s crucial to include:
To determine what content to include, ask yourself:
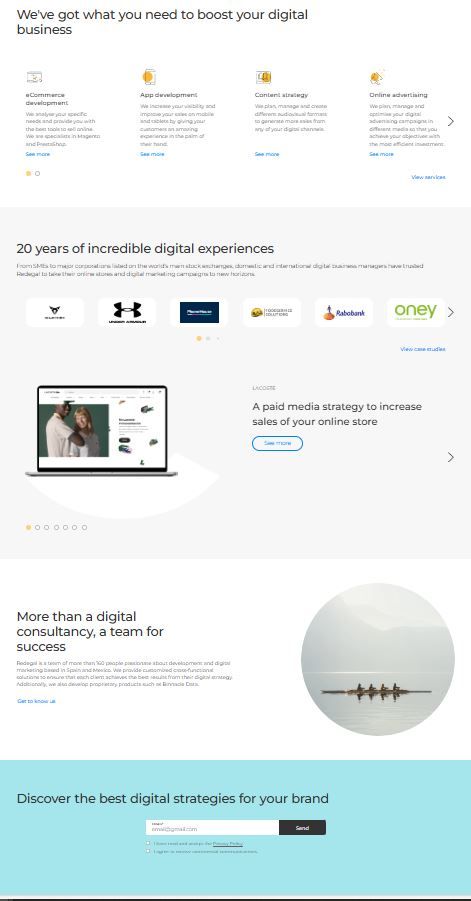
On Redegal’s website, the main content area is divided into sections aligned with the navigation menu. Each section not only details the services offered but also highlights client success stories, demonstrating what can be achieved.
The website footer is located at the bottom of each page and typically displays consistent information across multiple pages of the site. However, you can also design customized versions to suit your needs.
The footer is unique to each company and highlights key information such as legal notices, social media links, and important pages. It may also include CTAs or direct users to useful resources.
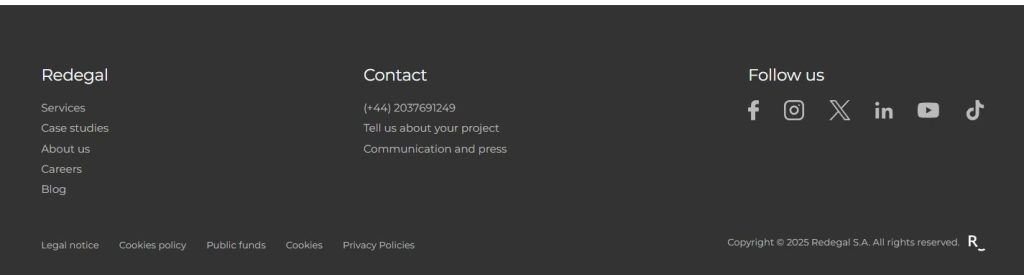
Here is an example of a footer so you can see how to adapt it to your company’s website. On the Redegal page, it consists of a menu, contact details, social media links, and a language translator. It also includes legal links and the registered trademark.
The sidebar is an important element located on the left or right side of the screen. This section provides a quick and efficient way to display additional information and important links to website visitors. The sidebar can contain a variety of elements, such as a search form, a social media feed, advertisements, popular links, recent blog posts, categories, tags, and more.
One of the main features of the sidebar is its prominent placement. Positioned in an easily accessible location for the user, it allows for faster and easier navigation through the website. Additionally, the elements in the sidebar are easily visible and accessible to the visitor.
Another important feature of the sidebar is its ability to display relevant and personalized content for the visitor. Users can choose which elements they prefer to see and which ones they don’t, allowing them to customize their browsing experience.
It is important to highlight that the sidebar should not be overwhelming or filled with unnecessary elements, as this can distract the user and make navigation harder. It is recommended to keep it clean and organized, with important and relevant elements that align with the website’s goals.
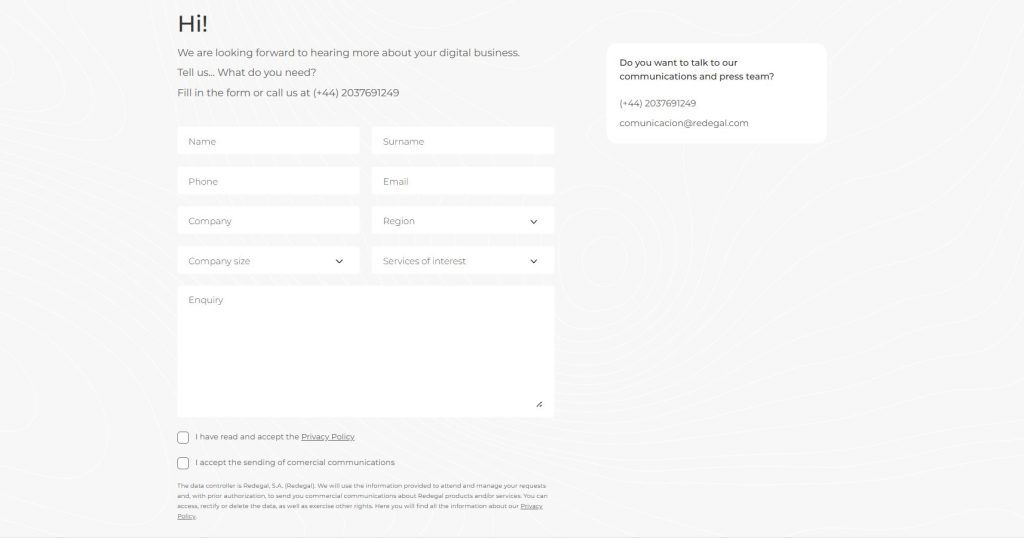
This element is crafted to capture information, so it must be easily accessible. The form allows users to reach out to your brand, and its questions should be brief and clear to gather meaningful insights.
Client accessing is crucial for any business. It allows for future contact with them and provides opportunities to offer promotions or new services.
A good form should include the following elements:
In our full digital company with a global reach, you can find forms like the one below. The fields can be customized, so look for those that best suit your company and its audience.
A good website structure has many important advantages that can help ensure the success of an online site. Here are some of the main benefits:
A good website structure ensures that visitors can easily find the information they need without spending time navigating a confusing or incoherent site. A clear and logical structure makes navigation easier for users, meaning visitors are more likely to stay on the site longer and return in the future.
Search engines use complex algorithms to rank web pages based on their relevance and usefulness. A clear and organized website structure can improve visibility in search results, increasing the chances of being found by users interested in the site’s topic.
With more and more internet users accessing websites from mobile devices, a good website structure becomes even more important. A well-designed structure ensures that navigation is easy and smooth across all types of devices, including smartphones and tablets.
If visitors can quickly and easily find the information they need, they are more likely to return to the site in the future and recommend it to others. It increases customer satisfaction by providing a positive and satisfying user experience.
A good website structure makes it easier to update and maintain the site. A clear and organized structure makes adding and updating content easier without changing the overall structure of the site.
Having social media profiles is a good decision for your company’s communication strategy, as long as content is tailored to the audience and characteristics of each platform. However, the formats and structures are standardized by the social network, with few customization options, not to mention the algorithm changes its policies and that can affect the content shared.
On the other hand, a website is not dependent on another company’s designs and allows for both content and structure customization, using various formats with greater creative freedom.
First, it’s essential to clearly understand why you are building the website and what you want to achieve with it. To answer these questions, you can refer to your brand’s goals. It’s also important to review your target audience, corporate identity, and the sections you want to include.
You need to find the Content Management System (CMS) that best suits your company. Consider which features you want it to have, such as content scheduling, multi-language options, or SEO optimization features. The limitations and possibilities of each CMS will affect the design of each part of your website.
Follow the guidelines for the elements to include in the menu and footer. Try to consider SEO and UX criteria when doing this. If you need help, we can support you. Shall we talk?
Now is the time to incorporate content into the body of the page. Depending on the type of page, you may need to include product listings, blog texts, etc. Define each content type to ensure a personalized yet standardized design for each one. At Redegal, we have a web design and development team that can help you through this process, designing and creating a website that fits your business and your audience’s needs.
Incorporate the content into the structure you’ve created and validate it with the other people involved in the design process. If possible, validate with users as well.
Remember that the display of each part of the page is not the same on computers as it is on mobile devices, and it must function correctly in both cases.
At Redegal, we’ve been helping our clients create their ideal website, tailored to their business needs, for 20 years. If you want to learn how to improve your website’s structure to get the most out of it, count on our team! Shall we talk?
You may be interested in our latest posts

Redegal, Google Partner Premier agency 2025
Intelligent Dynamic Feeds: how to analyse your catalogue with AI in seconds using Boostic.cloud

Follow Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) to increase your sales

What is lead nurturing and how to do it?
Discover the best digital strategies for your brand
Hi!
We are looking forward to hearing more about your digital business.
Tell us... What do you need?
Fill in the form or call us at (+44) 2037691249